FISH OIL
Help on accessing alternative formats, such as Portable Document Format (PDF), Microsoft Word and PowerPoint (PPT) files, can be obtained in the alternate format help section.
This monograph is intended to serve as a guide to industry for the preparation of Product Licence Applications (PLAs) and labels for natural health product market authorization. It is not intended to be a comprehensive review of the medicinal ingredient.
There are many N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, popularly known as omega-3 acids/ω-3 fatty acids (Ph.Eur. 2023). This monograph is specific to eicosapentaenoic acid (C20:5 n-3; EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (C22:6 n-3; DHA).
Notes
- This monograph only covers naturally-occurring fatty acids in fish oil with both EPA and DHA. Fish oils can be concentrated but not spiked with additional fatty acids.
- Text in parentheses is additional optional information which can be included on the PLA and product label at the applicant's discretion.
- The solidus (/) indicates that the terms and/or statements are synonymous. Either term or statement may be selected by the applicant.
Date
March 28, 2024
Proper name(s), Common name(s), Source information
| Proper name(s) | Common name(s) | Source information | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source material(s)1 | Part(s) | |||
| Fish oil | Fish oil |
|
Whole | |
References: Proper name: BP 2023, Ph.Eur. 2023; Common name: BP 2023, Ph.Eur. 2023; Source information: BP 2023, Ph.Eur. 2023, Froese and Pauly 2022.
1Corresponds to oil from the whole body of one or more of species of the families listed in Table 1 in its natural and/or concentrated triglyceride/triacylglycerol form and/or its concentrated esterified form (BP 2023; Ph.Eur. 2023; Froese and Pauly 2022). The species common names and not the family could be listed on the label.
2For fish oils including species of Gadidae as a source material, the vitamin A and D content should be tested to ensure that the daily maximum amounts meet the Multi-Vitamin/Mineral Supplements monograph for each age group.
Route of Administration
Oral
Dosage Form(s)
This monograph excludes foods or food-like dosage forms as indicated in the Compendium of Monographs Guidance Document.
Acceptable dosage forms by age group:
Children 1-2 years:The acceptable dosage forms are limited to emulsion/suspension and solution/liquid preparations (Giacoia et al. 2008; EMA/CHMP 2006).
Children 3-5 years:The acceptable dosage forms are limited to chewables, emulsion/ suspension, powders and solution/liquid preparations (Giacoia et al. 2008; EMA/CHMP 2006).
Children 6-11 years, Adolescents 12-17 years, and Adults 18 years and older: Acceptable dosage forms for this age category and specified route of administrationoral use are indicated in the Compendium of Monographs Guidance Document.dosage form drop-down list of the web-based Product Licence Application form for Compendial applications.
Use(s) or Purpose(s)
Products providing 100-5,000 mg eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), per day
- Source of omega-3 fatty acids for the maintenance of good health (EFSA 2012; Simopoulos 2007; Oh 2005; IOM 2002; Simopoulos 1999).
- Source of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) (EFSA 2012; Simopoulos 2007; Oh 2005; IOM 2002; Simopoulos 1999) for the maintenance of good health
Products providing 150-5,000 mg EPA and DHA including at least 100 mg DHA, per day
- Helps support/maintain cognitive health (EFSA 2012; van de Rest et al. 2008; Freund-Levi et al. 2006; Fontani et al. 2005a,b; Haag 2003; Morris et al. 2003; IOM 2002).
- Helps support/maintain brain function (EFSA 2012; van de Rest et al. 2008; Freund-Levi et al. 2006; Fontani et al. 2005a,b; Haag 2003; Morris et al. 2003; IOM 2002).
Products for children up to 12 years old and providing 200-2,000 mg EPA and DHA including at least 150 mg DHA, per day
Helps support/maintain (healthy) development of brain/(and), eyes/(and) nerves in children up to 12 years of age (Marszalek and Lodish 2005; Haag 2003; IOM 2002; Giedd et al. 1999; Mills 1999).
Products providing 200-5,000 mg EPA and DHA, per day
- Helps support/maintain (normal) heart/cardiovascular health (EFSA 2012; Oh 2005; Wang et al. 2004; Leaf et al. 2003; Kris-Etherton et al. 2002).
- Helps support/maintain (normal) heart/cardiovascular function (EFSA 2012; Oh 2005; Wang et al. 2004; Leaf et al. 2003; Kris-Etherton et al. 2002).
Products providing 1,000-5,000 mg EPA and DHA, per day
- Helps reduce (blood) triglyceride(s)/triacylglycerol(s) (levels) (EFSA 2012; Oh 2005; Balk et al. 2004; Hooper et al. 2004; Nilsen et al. 2001; Sirtori et al. 1998).
- Helps support/maintain normal (blood) triglyceride/triacylglycerol levels (EFSA 2012; Oh 2005; Balk et al. 2004; Hooper et al. 2004; Nilsen et al. 2001; Sirtori et al. 1998).
Products for adults and providing 2,800-5,000 mg EPA and DHA, per day and containing a ratio of EPA:DHA between 0.5:1 and 2:1
In conjunction with conventional therapy, helps reduce the pain of rheumatoid arthritis in adults (EFSA 2012; Volker et al. 2000; Sköldstam et al. 1992).
Products providing 1,500-5,000 mg EPA and DHA including at least 1000 mg EPA, per day
Helps promote healthy mood balance (EFSA 2012; Nemets et al. 2006; Sontrop and Campbell 2006; Fontani et al. 2005a,b; Zanarini and Frankenburg 2003; Peet and Horrobin 2002; Stoll et al. 1999).
Notes:
- The above uses can be combined on the product label (e.g. Helps reduce triglycerides and maintain cardiovascular health).
- The terms 'Helps' or 'Helps to' can be used interchangeably on the label.
Dose(s)
Subpopulation(s)
As specified below.
Quantity(ies)
Method of preparation: Standardized fixed oil
In addition to the quantity of fish oil, the potency information must be expressed as the quantity (milligrams) and/or percent (%) of EPA and DHA (% w/w) relative to the total quantity of fish oil.
| Subpopulation(s) | EPA+DHA (mg/day) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum1 | Maximum2 | ||
| Children | 1-8 years | 100 | 1,500 |
| 9-11 years | 100 | 2,000 | |
| Adolescents | 12-13 years | 100 | 2,000 |
| 14-17 years | 100 | 2,500 | |
| Adults | 18 years and older | 100 | 5,000 |
1Restrictions to minimum dose may apply according to Use(s) or Purpose(s)
section
above.
2Adult maximum dose of EPA + DHA is supported by US FDA 2019 and EFSA 2012.
Children and adolescent maximum doses are calculated as a fraction of the
adult
dose, are relative to body weight and caloric intake.
Direction(s) for use
No statement required.
Duration(s) of Use
No statement required.
Risk Information
Caution(s) and warning(s)
Pain of rheumatoid arthritis
Ask a health care practitioner/health care provider/health care professional/doctor/physician if symptoms worsen.
Healthy mood balance
Ask a health care practitioner/health care provider/health care professional/doctor/physician before use if you have psychological disorders such as anxiety or depression.
Contraindication(s)
No statement required.
Known adverse reaction(s)
No statement required.
Non-medicinal ingredients
Must be chosen from the current Natural Health Products Ingredients Database (NHPID) and must meet the limitations outlined in the database.
Storage conditions
Must be established in accordance with the requirements described in the Natural Health Products Regulations.
All products, except those encapsulated
Refrigerate after opening (Wille and Gonus 1989).
All products (information for industry; not for labelling)
To be packaged in airtight container, protected from light (Ph.Eur. 2023; USP-NF 2023).
Specifications
- The finished product specifications must be established in accordance with the requirements described in the Natural and Non-prescription Health Products Directorate (NNHPD) Quality of Natural Health Products Guide.
- The medicinal ingredient must comply with the requirements outlined in the NHPID. Peroxide, anisidine, and totox values of fish oil and omega-3 fatty acids derived from fish oil must be in accordance with the methods set out by the Association of Analytical Community (AOAC) and/or Pharmacopoeial analytical methods. These specifications are necessary to ensure the oxidative stability of the fish oil and the omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil (HC 2015). The maximum peroxide value (PV) must be 5 mEq/kg, the maximum anisidine value (AV) must be 20 while the maximum Totox value must be 26 (calculated as 2 X PV + AV).
- The dioxins, polychlorinated dibenzo-para-dioxins (PCDDs) and polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs); the dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls (DL PCBs); and the polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are contaminants in oils from marine sources. Testing for these contaminants is required. As indicated in the Quality of Natural Health Products Guide, testing should be performed using appropriate analytical methods, such as method No. 1613 revision B of the Environmental Protection Agency for PCDDs and PCDFs and method No. 1668B of the Environmental Protection Agency for chlorinated biphenyl congeners. Licence holders are advised to consult the Commission of the European Communities documents on dioxins and dioxin-like PCB contaminants in marine oil for further information. Refer to the Quality of Natural Health Products Guide for more information on the acceptable limits of dioxins and dioxin-like PCBs.
- For fish oils including Gadidae as a source material, the vitamin A and D content should be tested to ensure that their respective daily maximum amounts meet the Multi-Vitamin/Mineral Supplements monograph for each age group.
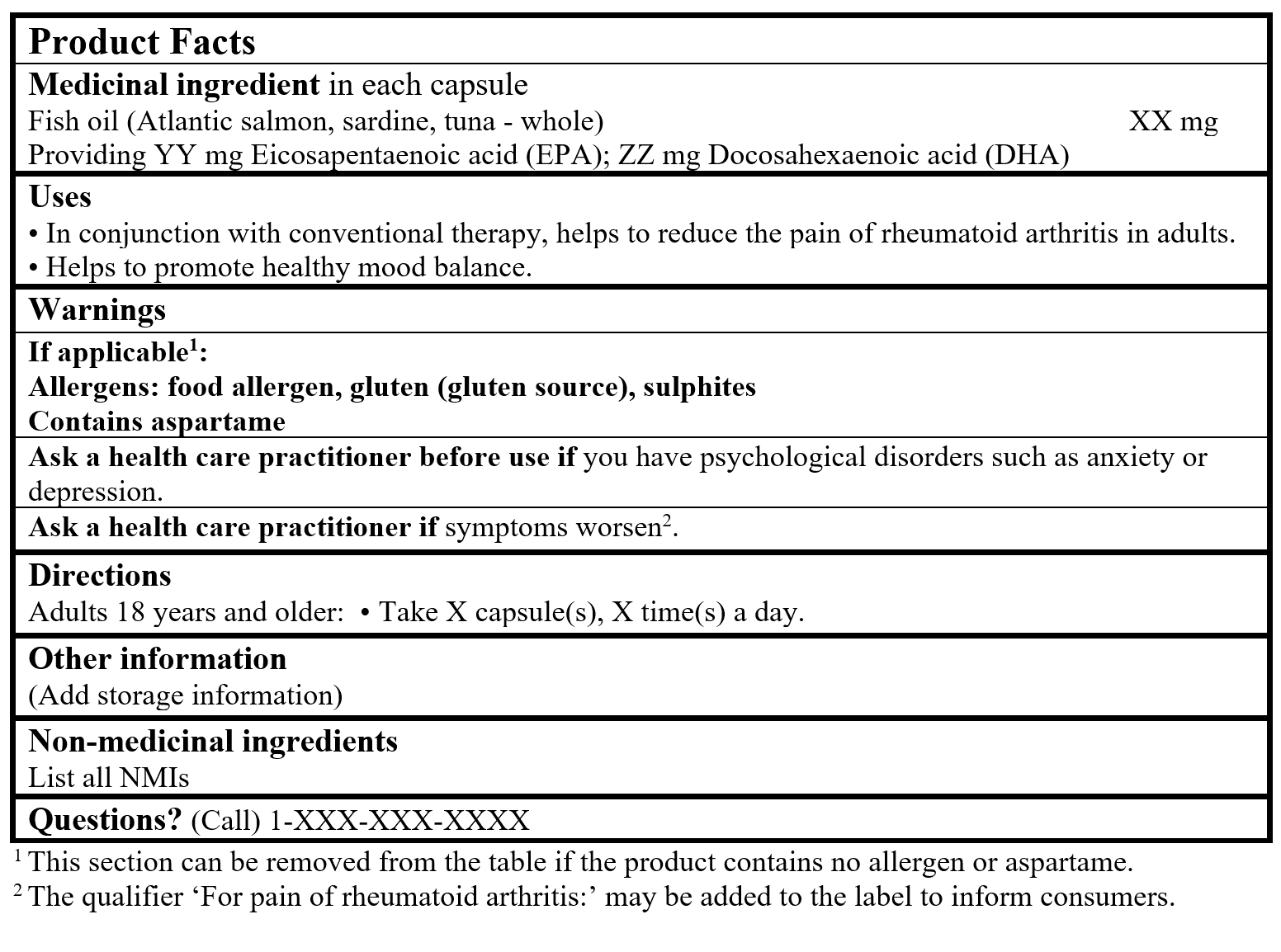
EXAMPLE OF PRODUCT FACTS:
Consult the Guidance Document, Labelling of Natural Health Products for more details.
References Cited
- Balk E, Chung M, Lichtenstein A, Chew P, Kupelnick B, Lawrence A, DeVine D, Lau J. 2004 Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Intermediate Markers of Cardiovascular Disease. Summary, Evidence Report/Technology Assessment No. 93. AHRQ Publication No. 04-E010-1. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
- BP 2023: British Pharmacopoeia 2023. London (GB): The Stationary Office on behalf of the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA); 2023.
- EFSA 2012: European Food Safety Authority. Scientific Opinion: Scientific opinion on the tolerable upper intake level of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and docosapentaenoic acid (DPA). EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). EFSA Journal 2012;10(7):2815. [Accessed 2023 March 07]. Available from: http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/doc/2815.pdf
- EMA/CHMP 2006: European Medicines Agency: Pre-authorization Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use. Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use. Reflection Paper: Formulations of choice for the paediatric population. [Accessed 2023 March 07]. Available from: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/reflection-paper-formulations-choice-paediatric-population_en.pdf.
- EU 2011: European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) No 1259/2011 of 2 December 2011 amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 as regards maximum levels for dioxins, dioxin-like PCBs and non dioxin-like PCBs in foodstuffs. Official Journal of the European Union L 320/18 3.12.2011. [Accessed 2023 March 07]. Available from: https://faolex.fao.org/docs/pdf/eur108087.pdf
- Fontani G, Corradeschi F, Felici A, Alfatti F, Migliorini S, Lodi L. 2005a. Cognitive and physiological effects of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation in healthy subjects. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 35(11):691-699.
- Fontani G, Corradeschi F, Felici A, Alfatti F, Bugarini R, Fiaschi AI, Cerretani D, Montorfano G, Rizzo AM, Berra B. 2005b. Blood profiles, body fat and mood state in healthy subjects on different diets supplemented with omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 35(8):499-507.
- Freund-Levi Y, Eriksdotter-Jonhagen M, Cederholm T, Basun H, Faxen-Irving G, Garlind A, Vedin I, Vessby B, Wahlund LO, Palmblad J. 2006. ω-3 fatty acid treatment in 174 patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer disease: omegAD study. Archives of Neurology 63(10):1402-1408.
- Froese R, Pauly D, editors. 2022. FishBase: A Global Information System on Fishes. Penang (MY): WorldFish Center. [Accessed 2023 March 07]. Available from: http://www.fishbase.org
- Giacoia GP, Taylor-Zapata P, Mattison D. Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Pediatric Formulation Initiative: selected reports from working groups. Clinical Therapeutics 2008; 30(11):2097-2101.
- Giedd JN, Blumenthal J, Jeffries NO, Castellanos FX, Liu H, Zijdenbos A, Paus T, Evans AC, Rapoport JL. 1999. Brain development during childhood and adolescence: a longitudinal MRI study. Nature Neuroscience 2(10):861-863.
- Haag M. 2003. Essential fatty acids and the brain. The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry 48(3):195-203.
- HC 2015: Health Canada. Quality of Natural Health Products Guide. Version 3.1 Ottawa (ON): Natural Health Products Directorate, Health Canada. [Accessed 2023 March 07]. Available from: https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/drugs-health-products/natural-non-prescription/legislation-guidelines/guidance-documents/quality-guide.html.
- Hooper L, Thompson RL, Harrison RA, Summerbell CD, Moore H, Worthington HV, Durrington PN, Ness AR, Capps NE, Davey Smith G, Riemersma RA, Ebrahim SBJ. 2004. Omega 3 fatty acids for prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Issue 4. Art. No.: CD003177. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003177.pub2.
- IOM 2002: Panel on Macronutrients, Panel on the Definition of Dietary Fiber, Subcommittee on Upper Reference Levels of Nutrients, Subcommittee on Interpretation and Uses of Dietary Reference Intakes, and the Standing Committee on the Scientific Evaluation of Dietary Reference Intakes. Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine. 2002. Dietary Reference Intakes for Energy, Carbohydrate, Fiber, Fat, Fatty Acids, Cholesterol, Protein, and Amino Acids. Washington (DC): The National Academies Press.
- Kris-Etherton PM, Harris WS, Appel LJ, American Heart Association Nutrition Committee. 2002. Fish consumption, fish oil, omega-3 fatty acids, and cardiovascular disease. Circulation 106(21):2747-2757.
- Leaf A, Kang JX, Xiao YF, Billman GE. 2003. Clinical prevention of sudden cardiac death by n3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and mechanism of prevention of arrhythmias by n-3 fish oils. Circulation 107(21):2646-2652.
- Marszalek JR, Lodish HF. 2005. Docosahexaenoic acid, fatty acid-interacting protein, and neuronal function: breastmilk and fish are good for you. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology 21:633-657.
- Mills MD. 1999. The eye in childhood. American Family Physician 60(3):907-918.
- Morris MC, Evans DA, Bienias JL, Tangney CC, Bennett DA, Wilson RS, Aggarwal N, Schneider J. 2003. Consumption of fish and n-3 fatty acid and risk of incident alzheimer disease. Archives of Neurology 60(7):940-946.
- Nemets H, Nemets B, Apter A, Bracha Z, Belmaker RH. 2006. Omega-3 treatment of childhood depression: a controlled, double-blind pilot study. The American Journal of Psychiatry 163(6):1098-1100.
- Nilsen DW, Albrektsen G, Landmark K, Moen S, Aarsland T, Woie L. 2001. Effects of a highdose concentrate of n-3 fatty acids or corn oil introduced early after an acute myocardial infarction on serum triacylglycerol and HDL cholesterol. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 74(1):50-56.
- Oh R. 2005. Practical applications of fish oil (Ω-3 fatty acids) in primary care. The Journal of the American Board of Family Practice 18(1):28-36.
- Peet M, Horrobin DF. 2002. A dose-ranging study of the effects of ethyl-eicosapentaenoate in patients with ongoing depression despite apparently adequate treatment with standard drugs. Archives of General Psychiatry 59(10):913-919.
- Ph.Eur. 2023: European Pharmacopoeia. 11th edition. Strasbourg (FR): Directorate for the Quality of Medicines and HealthCare of the Council of Europe (EDQM), 2023.
- Simopoulos AP. 2007. Omega-3 fatty acids and athletics. Current Sports Medicine Reports 6(4):230-236.
- Simopoulos AP. 1999. Essential fatty acids in health and chronic disease. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 70(Suppl 3):560S-569S.
- Sirtori CR, Crepaldi G, Manzato E, Mancini M, Rivellese A, Paoletti R, Pazzucconi F, Pamparana F, Stragliotto E. 1998. One-year treatment with ethyl esters of n-3 fatty acids in patients with hypertriglyceridemia and glucose intolerance: reduced triglyceridemia, total cholesterol and increased HDL-C without glycemic alterations. Atherosclerosis 137(2):419-427.
- Sköldstam L, Börjesson O, Kjällman A, Seiving B, Akesson B. 1992. Effect of six months of fish oil supplementation in stable rheumatoid arthritis. A double-blind, controlled study. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 21(4):178-185.
- Sontrop J, Campbell MK. 2006. ?-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and depression: a review of the evidence and a methodological critique. Preventative Medicine 42(1):4-13.
- Stoll AL, Locke CA, Marangell LB, Severus WE. 1999. Omega-3 fatty acids and bipolar disorder: a review. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes, and Essential Fatty Acids 60(5-6):329-337.
- US FDA 2019. FDA Announces new qualified health claims for EPA and DHA Omega-3 consumption and the risk of hypertension and coronary disease; and associated link: FDA Response to Petition for Qualified Health Claim that EPA and DHA Omega-3 Consumption May Reduce Risk of Hypertension. [Accessed 2024 February 22]. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/food/cfsan-constituent-updates/fda-announces-new-qualified-health-claims-epa-and-dha-omega-3-consumption-and-risk-hypertension-and
- USP-NF 2023: United States Pharmacopeia and the National Formulary. Rockville (MD): The United States Pharmacopeial Convention; https://online.uspnf.com.
- van de Rest O, Geleijnse JM, Kok JF, van Staveren WA, Dullemeijer C, OldeRikkert MGM, Beekman ATF, de Groot CPGM. 2008. Effect of fish oil on cognitive performance in older subjects: a randomized, controlled trial. Neurology 71(6):430-438.
- Volker D, Fitzgerald P, Major G, Garg M. 2000. Efficacy of fish oil concentrate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. The Journal of Rheumatology 27(10):2343-2346.
- Wang C, Chung M, Balk E, Kupelnick B, DeVine D, Lawrence A, Lichtenstein A, Lau J. 2004. Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Cardiovascular Disease. Summary, Evidence Report/Technology Assessment No. 94. AHRQ No. 04-E009-2. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
- Wille HJ, Gonus P. 1989. Preparation of Fish Oil for Dietary Applications. In: Galli C, Simopolous AP, editors. Dietary ω3 and ω6 Fatty Acids. Biological Effects and Nutritional Essentiality. New York (NY): Plenum Press.
- Zanarini MC, Frankenburg FR. 2003. Omega-3 fatty acid treatment of women with borderline personality disorder: a double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. The American Journal Psychiatry 160(1):167-169.
References Reviewed
- Ackman RG. 1992. The absorption of fish oils and concentrates. Lipids 27(11):858-862.
- Aggett PJ, Antoine JM, Asp NG, Bellisle F, Contor L, Cummings JH, Howlett J, Müller DJ, Persin C, Pijls LT, Rechkemmer G, Tuijtelaars S, Verhagen H. 2005. PASSCLAIM: consensus on criteria. European Journal of Nutrition 44(Suppl 1):i5-i30.
- Agostini C, Massetto N, Biasucci G, Rottoli A, Bonvissuto M, Bruzzese MG, Giovannini M, Riva E. 2000. Effects of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation on fatty acid status and visual function in treated children with hyperphenylalaninemia. Journal of Pediatrics 137(4):504-509.
- Ahmed AA, Holub BJ. 1984. Alteration and recovery of bleeding times, platelet aggregation and fatty acid composition of individual phospholipids in platelets of human subjects receiving a supplement of cod liver oil. Lipids 19(8):617-624.
- Allen KG, Harris MA. 2001. The role of n-3 fatty acids in gestation and parturition. Experimental Biology and Medicine 226(6):498-506.
- Angerer P, Kothny W, Störk S, von Schacky C. 2002. Effect of dietary supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids on progression of atherosclerosis in carotid arteries. Cardiovascular Research 54(1):183-190.
- Annuzzi G, Rivellese A, Capaldo B, Di Marino L, Iovine C, Marotta G, Riccardi G. 1991. A controlled study on the effects of n-3 fatty acids on lipid and glucose metabolism in non-insulindependent diabetic patients. Atherosclerosis 87(1):65-73.
- Appel LJ, Miller ER, Seidler AJ, Whelton PK. 1993. Does supplementation of diet with 'fish oil' reduce blood pressure? Archives of Internal Medicine 153(12):1429-1438.
- Bairati I, Roy L, Meyer F. 1992. Effects of a fish oil supplement on blood pressure and serum lipids in patients treated for coronary artery disease. The Canadian Journal of Cardiology 8(1):41-46.
- Beblo S, Reinhardt H, Demmelmair H, Muntau A, Koletzko B. 2007. Effects of fish oil supplementation on fatty acid status, coordination, and fine motor skills in children with phenylketonuria. Journal of Pediatrics 150(5):479-484.
- Beblo S, Reinhardt H, Muntau AC, Mueller-Felber W, Roscher AA, Koletzko B. 2001. Fish oil supplementation improves visual evoked potentials in children with phenylketonuria. Neurology 57(8):1488-1491.
- Bender NK, Kraynak MA, Chiquette E, Linn WD, Clark GM, Bussey HI. 1998. Effects of marine fish oils on the anticoagulation status of patients receiving chronic warfarin therapy. Journal of Thrombosis and Thrombolysis 5(3):257-261.
- Berbert AA, Kondo CR, Almendra CL, Matsuo T, Dichi I. 2005. Supplementation of fish oil and olive oil in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Nutrition 21(2):131-136.
- Birberg-Thornberg U, Karlsson T, Gustafsson PA, Duchen K. 2006. Nutrition and theory of mind - the role of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) in the development of theory of mind. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes and Essential Fatty Acids 75(1):33-41.
- Birch EE, Castaneda YS, Wheaton DH, Birch DG, Uauy RD, Hoffman DR. 2005. Visual maturation of term infants fed long-chain polyunsaturated fatty-acid supplemented or control formula for 12 mo. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 81(4):871-879.
- Birch EE, Garfield S, Hoffman DR, Uauy R, Birch DG. 2000. A randomized controlled trial of early long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids and mental development in term infants. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 42(3):174-181.
- Birch EE, Hoffman DR, Castañeda YS, Fawcett SL, Birch DG, Uauy RD. 2002. A randomized controlled trial of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation of formula in term infants after weaning at 6 wk of age. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 75(3):570-580.
- Blonk MC, Bilo HJ, Nauta JJ, Popp-Snijders C, Mulder C, Donker AJ. 1990. Dose-response effects of fish-oil supplementation in healthy volunteers. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 52(1):120-127.
- Bønaa KH, Bjerve KS, Nordøy A. 1992. Docosahexaenoic and eicosapentaenoic acids in plasma phospholipids are divergently associated with high density lipoprotein in humans. Arteriosclerosis and Thrombosis 12(6):675-681.
- Bonnema SJ, Jespersen LT, Marving J, Gregersen G. 1995. Supplementation with olive oil rather than fish oil increases small arterial compliance in diabetic patients. Diabetes, Nutrition & Metabolism 8(2):81-87.
- Bourre JM. 2006. Effects of nutrients (in food) on the structure and function of the nervous system: update on dietary requirements for brain. Part 2: macronutrients. Journal of Nutritional Health and Aging 10(5):386-399.
- Brinker F. 2001. Herb Contraindication and Drug Interactions. 3rd edition. Sandy (OR): Eclectic Medical Publications.
- Buckley MS, Goff AD, Knapp WE. 2004. Fish oil interaction with warfarin. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 38(1):50-53.
- Buckley R, Shewring B, Turner R, Yaqoob P, Minihane AM. 2004. Circulating triacylglycerol and apoE levels in response to EPA and docosahexaenoic acid supplementation in adult human subjects. The British Journal of Nutrition 92(3):477-483.
- Burgess JR, Stevens L, Zhang W, Peck L. 2000. Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 71(Suppl l):327S-330S.
- Cairns JA, Gill J, Morton B, Roberts R, Gent M, Hirsh J, Holder D, Finnie K, Marquis JF, Naqvi S, Cohen E. 1996. Fish oils and low-molecular-weight heparin for the reduction of restenosis after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. The EMPAR Study. Circulation 94(7):1553-1560.
- Calder PC. 2004. n-3 fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: evidence explained and mechanisms explored. Clinical Science 107(1):1-11.
- Calder PC. 2006. n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, inflammation, and inflammatory diseases. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 83(Suppl 6):1505S-1519S.
- Calò L, Bianconi L, Colivicchi F, Lamberti F, Loricchio ML, de Ruvo E, Meo A, Pandozi C, Staibano M, Santini M. 2005. N-3 fatty acids for the prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a randomized, controlled trial. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 45(10):1723-1728.
- Calon F, Lim GP, Yang F, Morihara T, Teter B, Ubeda O, Rostaing P, Triller A, Salem N Jr, Ashe KH, Frautschy SA, Cole GM. 2004. Docosahexaenoic acid protests from dendritic pathology in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model. Neuron 43(5):596-599.
- Carlson SE. 1996. Arachidonic acid status of human infants: influence of gestational age at birth and diets with very long chain n-3 and n-6 fatty acids. The Journal of Nutrition 126(Suppl 4):1092S-1098S.
- Carlson SE, Werkman SH, Peeples JM, Cooke RJ, Tolley EA. 1993. Arachidonic acid status correlates with first year growth in preterm infants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 90(3):1073-1077.
- Carroll DN, Roth MT. 2002. Evidence for the cardioprotective effects of omega-3 fatty acids. The Annals of Pharmacotherapy 36(12):1950-1956.
- Cazzola R, Russo-Volpe S, Miles EA, Rees D, Banerjee T, Roynette CE, Wells SJ, Goua M, Wahle KW, Calder PC, Cestaro B. 2007. Age- and dose-dependent effects of an eicosapentaenoic acid-rich oil on cardiovascular risk factors in healthy male subjects. Atherosclerosis 193(1):159-167.
- Chee KM, Gong JX, Rees DM, Meydani M, Ausman L, Johnson J, Siguel EN, Schaefer EJ. 1990. Fatty acid content of marine oil capsules. Lipids 25(9):523-528.
- Cleary MA, Feillet F, White FJ, Vidailhet M, MacDonald A, Grimsley A, Maurin N, Ogier de Baulny H, Rutherford PJ. 2006. Randomised controlled trial of essential fatty acid supplementation in phenylketonuria. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 60(7):915-920.
- Cleland LG, French JK, Betts WH, Murphy GA, Elliot MJ. 1988. Clinical and biochemical effects of dietary fish oil supplements in rheumatoid arthritis. The Journal of Rheumatology 15(10):1471-1475.
- Colter AL, Cutler C, Meckling KA. 2008. Fatty acid status and behavioural symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in adolescents: a case-control study. Nutrition Journal 7:8.
- Commission of the European Communities. Commission Regulation (EC) No 1883/2006 of 19 December 2006 laying down the methods of sampling and analysis for the official control of levels of dioxins and dioxin-like PCBs in certain foodstuffs. Official Journal of the European Union L 364/32 20.12.2006. [Accessed 2023 March 07]. Available from: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2006:364:0032:0043:EN:PDF
- Commission of the European Communities. Commission Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Official Journal of the European Union L 364/5 20.12.2006. [Accessed 2023 March 07]. Available from: http://eurlex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2006:364:0005:0024:EN:PDF
- Commission of the European Communities. Commission Regulation (EC) No 199/2006 of 3 February 2006 amending Regulation (EC) No 466/2001 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs as regards dioxins and dioxin-like PCBs. Official Journal of the European Union L 32/34 4.2.2006. [Accessed 2023 March 07]. Available from: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2006:032:0034:0038:EN:PDF
- Commission of the European Communities. Commission Directive 2004/44/EC of 13 April 2004 amending Directive 2002/69/EC laying down the sampling methods and the methods of analysis for the official control of dioxins and the determination of dioxin-like PCBs in foodstuffs.Official Journal of the European Union L 113/17 20.4.2004. [Accessed 2023 March 07]. Available from: http://eur- lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2002:209:0005:0014:EN:PDF
- Commission of the European Communities. Commission Regulation (EC) No 466/2001 of 8 March 2001 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Official Journal of the European Union L 77/1 16.3.2001. [Accessed 2023 March 07]. Available from: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2001:077:0001:0013:EN:PDF
- Council of the European Union. Commission Regulation (EC) No 2375/2001 of 29 November 2001 amending Regulation (EC) No 466/2001 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Official Journal of the European Communities L 321/1 6.12.2001. [Accessed 2023 March 07]. Available from: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2001:321:0001:0005:EN:PDF
- Conklin SM, Gianaros PJ, Brown SM, Yao JK, Hariri AR, Manuck SB, Muldoon MF. 2007. Long-chain omega-3 fatty acid intake is associated positively with corticolimbic gray matter volume in healthy adults. Neuroscience Letter 421(3):209-212.
- Connor WE, DeFrancesco CA, Connor SL. 1993. N-3 fatty acids from fish oil. Effects on plasma lipoproteins and hypertriglyceridemic patients. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 683:16-34.
- Connor WE, Prince MJ, Ullmann D, Riddle M, Hatcher L, Smith FE, Wilson D. 1993. The hypotriglyceridemic effect of fish oil in adult-onset diabetes without adverse glucose control. Annals of the New York Academy of Science 683:337-340.
- Cunnane S, Drevon CA, Harris B, Sinclair A, Spector A. 2004. Recommendations for intake of polyunsaturated fatty acids in healthy adults. Devon (GB): International Society for the Study of Fatty Acids and Lipids. [Accessed 2023 March 07]. Available from: https://www.ojp.gov/ncjrs/virtual-library/abstracts/recommendations-intake-polyunsaturated-fatty-acids-healthy-adults
- Dangour AD, Uauy R. 2008. N-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids for optimal function during brain development and ageing. Asian Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition 17(Suppl 1):185-188.
- De Groot RHM, Hornstra G, Jolles J. 2007. Exploratory study into the relation between plasma phospholipid fatty acid status and cognitive performance. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes, and Essential Fatty Acids 76(3):165-172.
- Deutch B, Jørgensen EB, Hansen JC. 2000. Menstrual discomfort in Danish women reduced by dietary supplements of omega-3 PUFA and B12 (fish oil or seal oil capsules). Nutrition Research 20(5):621-631.
- Dokholyan RS, Albert CM, Appel LJ, Cook NR, Whelton PK, Hennekens CH. 2004. A trial of omega-3 fatty acids for prevention of hypertension. The American Journal of Cardiology 93(8):1041-1043.
- Dunstan JA, Mori TA, Barden A, Beilin LJ, Taylor AL, Holt PG, Prescott SL. 2003. Fish oil supplementation in pregnancy modifies neonatal allergen-specific immune responses and clinical outcomes in infants at high risk of atopy: a randomized, controlled trial. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 112(6):1178-1184.
- Dunstan JA, Roper J, Mitoulas L, Hartmann PE, Simmer K, Prescott SL. 2004. The effect of supplementation with fish oil during pregnancy on breast milk immunoglobulin A, soluble CD14, cytokine levels, and fatty acid composition. Clinical and Experimental Allergy 34(8):1237-1242.
- Engeset D, Alsaker E, Lund E, Welch A, Khaw KT, Clavel-Chapelon F, Thiébaut A, Chajès V, Key TJ, Allen NE, Amiano P, Dorronsoro M, Tjønneland A, Stripp C, Peeters PH, van Gils CH, Chirlaque MD, Nagel G, Linseisen J, Ocké MC, Bueno-de-Mesquita1 HB, Sacerdote C, Tumino R, Ardanaz E, Sánchez MJ, Panico S, Palli D, Trichopoulou A, Kalapothaki V, Benetou V, Quirós JR, Agudo A, Overvad K, Bjerregaard L, Wirfält E, Schulz M, Boeing H, Slimani N, Riboli E. 2006. Fish consumption and breast cancer risk. The European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC). International Journal of Cancer 119(1):175-182.
- Engler MM, Engler MB, Malloy MJ, Paul SM, Kulkarni KR, Mietus-Snyder ML. 2005. Effect of docosahexaenoic acid on lipoprotein subclasses in hyperlipidemic children (the EARLY study). The American Journal of Cardiology 95(7):869-871.
- Eritsland J. 2000. Safety considerations of polyunsaturated fatty acids. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 71(Suppl 1):197S-201S.
- Eritsland J, Arnesen H, Seljeflot I, Høstmark AT. 1995. Long-term metabolic effects of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in patients with coronary artery disease. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 61(4):831-836.
- Eritsland J, Arnesen H, Seljeflot I, Kierulf P. 1995. Long-term effects of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on haemostatic variables and bleeding episodes in patients with coronary artery disease. Blood Coagulation and Fibrinolysis 6(1):17-22.
- Eritsland J, Seljeflot I, Abdelnoor M, Arnesen H, Torjesen PA. 1994. Long-term effects of n-3 fatty acids on serum lipids and glycemic control. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation 54(4):273-280.
- European Commission. Commission Recommendation of 23 August 2011 on the reduction of the presence of dioxins, furans and PCBs in feed and food (2011/516/EU) Official Journal of the European Union L 218/23 24.8.2011. [Accessed 2023 March 07]. Available from: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2011:218:0023:0025:EN:PDF
- European Food Safety Authority. 2008. Scientific substantiation of a health claim related to Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) and Arachidonic Acid (ARA) and support of the neural development of the brain and eyes pursuant to Article 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. The EFSA Journal 794:1-11.
- European Food Safety Authority. 2008. Scientific substantiation of a health claim related to ?linolenic acid and linoleic acid and growth and development of children pursuant to Article 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. The EFSA Journal 783:1-9.
- Fitzpatrick KC. 2005. Invitational Consultation on Fatty Acids. Winnipeg (MB): Nutritech Consulting.
- Fortin PR, Lew RA, Liang MH, Wright EA, Beckett LA, Chalmers TC, Sperling RI. 1995. Validation of a meta-analysis: the effects of fish oil in rheumatoid arthritis. The Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 48(11):1379-1390.
- Frais AT. 2007. Depression and the causal role of specific memory system degenerations: Link may be supported by reported therapeutic benefits of omega 3 fatty acids. Medical Hypothesis 69(1):67-69.
- Frangou S, Lewis M, McCrone P. 2006. Efficacy of ethyl-eicosapentaenoic acid in bipolar depression: randomised double-blind placebo-controlled study. The British Journal of Psychiatry 188:46-50.
- Franzen D, Schannwell M, Oette K, Höpp HW. 1993. A prospective, randomized, and doubleblind trial on the effect of fish oil on the incidence of restenosis following PTCA. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Diagnosis 28(4):301-310.
- Freese R, Mutanen N. 1997. Alpha-linolenic acid and marine long-chain n-3 fatty acids differ only slightly in their effects on hemostatic factors in healthy subjects. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 66(3):591-598.
- Fregni F, Schachter SC, Pascual-Leone A. 2005. Review: Transcranial magnetic stimulation treatment for epilepsy: can it also improve depression and vice versa? Epilepsy and Behavior 7(2):182-189.
- Friedberg CE, Janssen MJ, Heine RJ, Grobbee DE. 1998. Fish oil and glycemic control in diabetes. A meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 21(4):494-500.
- Fux M, Benjamin J, Nemets B. 2004. A placebo-controlled crossover trial of adjunctive EPA in OCD. Journal of Psychiatric Research 38(3):323-325.
- Gadoth N. 2008. On fish oil and omega-3 supplementation in children: the role of such supplementation on attention and cognitive dysfunction. Brain and Development 30(5):309-312.
- Gapinski JP, VanRuiswyk JV, Heudebert GR, Schectman GS. 1993. Preventing restenosis with fish oils following coronary angioplasty: a meta-analysis. Archives of Internal Medicine 153(13):1595-1601.
- Geelen A, Brouwer IA, Schouten EG, Maan AC, Katan MB, Zock PL. 2005. Effects of n-3 fatty acids from fish on premature ventricular complexes and heart rate in humans. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 81(2):416-420.
- Geleijnse JM, Giltay EJ, Grobbee DE, Donders AR, Kok FJ. 2002. Blood pressure response to fish oil supplementation: metaregression analysis of randomized trials. Journal of Hypertension 20(8):1493-1499.
- Geusens P, Wouters C, Nijs J, Jiang Y, Dequeker J. 1994. Long-term effect of omega-3 fatty acid supplementation in active rheumatoid arthritis: a 12-month, double-blind, controlled study. Arthritis & Rheumatism 37(6):824-829.
- Goodnight SH, Harris WS, Connor WE. 1981. The effects of dietary omega-3 fatty acids on platelet composition and function in man: a prospective, controlled study. Blood 58(5):880-885.
- Grimsgaard S, Bonaa KH, Hansen JB, Nordøy A. 1997. Highly purified eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid in humans have similar triacylglycerol-lowering effects but divergent effects on serum fatty acids. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 66(3):649-659.
- Guivernau N, Meza N, Barja P, Roman O. 1994. Clinical and experimental study on the long-term effect of dietary gamma-linolenic acid on plasma lipids, platelet aggregation, thromboxane formation, and prostacyclin production. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes, and Essential Fatty Acids 51(5):311-316.
- Haglund O, Luostarinen R, Wallin R, Wibell L, Saldeen T. 1991. The effects of fish oil on triglycerides, cholesterol, fibrinogen and malondialdehyde in humans supplemented with vitamin European Journal of Nutrition 121(2):165-169.
- Hakkarainen R, Partonen T, Haukka J, Virtamo J, Albanes D, Lonnqvist J. 2004. Food and nutrient intake in relation to mental wellbeing. Nutritional Journal 3(14):1-5.
- Halldorsson TI, Meltzer HM, Thorsdottir I, Knudsen V, Olsen SF. 2007. Is high consumption of fatty fish during pregnancy a risk factor for fetal growth retardation? A study of 44,824 Danish pregnant women. American Journal of Epidemiology 166(6):687-696.
- Halliwell B, Chirico S. 1993. Lipid peroxidation: its mechanism, measurement, and significance. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 57(Suppl 5):715S-725S.
- Hamazaki T, Sawazaki S, Nagao Y, Kuwamori T, Yazawa K, Mizushima Y, Kobayashi M. 1998. Docosahexaenoic acid does not affect aggression of normal volunteers under nonstressful conditions. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Lipids 33(7):663-667.
- Hamazaki T, Sawazaki S, Itomura M, Asaoka E, Nagao Y, Nishimura N, Yazawa K, Kuwamori T, Kobayashi M. 1996. The effect of docosahexaenoic acid on aggression in young adults: a placebo-controlled double-blind study. Journal Clinical Investigation 97(4):1129-1134.
- Harel Z, Biro FM, Kottenhahn RK, Rosenthal SL. 1996. Supplementation with omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in the management of dysmenorrhea in adolescents. The American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 174(4):1335-1338.
- Harris WS. 2010. Omega-3 Fatty Acids. In: Coates PM, Betz JM, Blackman MR, Cragg GM, Levine M, Moss J, White JD, editors. Encyclopedia of Dietary Supplements. Second edition. New York (NY): Informa Healthcare.
- Harris WS. 2007. International recommendations for consumption of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids. The Journal of Cardiovascular Medicine 8(1):S50-S52.
- Harrison N, Abhyankar B. 2005. The mechanism of action of omega-3 fatty acids in secondary prevention post-myocardial infarction. Current Medical Research and Opinion 21(1):95-100.
- Health Canada. Food Rulings Proposal - EPA and DHA: Level of Addition to Foods. Ottawa (ON): Bureau of Nutritional Sciences, Health Canada; 2006.
- He K, Song Y, Daviglus ML, Liu K, Van Horn L, Dyer AR, Goldbourt U, Greenland P. 2004. Fish consumption and incidence of stroke: a meta-analysis of cohort studies. Stroke 35(7):1538-1542.
- Hendler SS, Rorvik D, editors. 2001. PDR for Nutritional Supplements, 1st edition. Montvale (NJ): Thomson PDR.
- Hibbeln JR, Ferguson TA, Blasbalg TL. 2006. Omega-3 fatty acid deficiencies in neurodevelopment, aggression and autonomic dysregulation: opportunities for intervention. International Review of Psychiatry 18(2):107-118.
- Hjerkinn EM, Seljeflot I, Ellingsen I, Berstad P, Hjermann I, Sandvik L, Arnesen H. 2005. Influence of long-term intervention with dietary counselling, long-chain n-3 fatty acid supplements, or both on circulating markers of endothelial activation in men with long-standing hyperlipidemia. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 81(3):583-589.
- Hodge W, Barnes D, Schachter HM, Pan Y, Lowcock EC, Zhang L, Sampson M, Morrison A, Tran K, Miguelez M, Lewin G. 2005. Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Eye Health. Summary, Evidence Report/Technology Assessment No. 117. AHRQ No. 05-E008-2. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
- Hodge L, Salome CM, Hughes JM, Liu-Brennan D, Rimmer J, Allman M, Pang D, Armour C, Woolcock AJ. 1998. Effect of dietary intake of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids on severity of asthma in children. European Respiratory Journal 11(2):361-365.
- Hoffman DR, Locke KG, Wheaton DH, Fish GE, Spencer R, Birth DG. 2004. A randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial of docosahexaenoic acid supplementation for X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. American Journal of Ophthalmology 137(4):704-718.
- Holguin F, Téllez-Rojo MM, Lazo M, Mannino D, Schwartz J, Hernández M, Romieu I. 2005. Cardiac autonomic changes associated with fish oil vs soy oil supplementation in the elderly. Chest 127(4):1102-1107.
- Hornstra G. 2000. Essential fatty acids in mothers and their neonates. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 71(Suppl 5):1262S-1269S.
- Iacoviello L, Amore C, De Curtis A, Tacconi MT, de Gaetano G, Cerletti C, Donati MB. 1992. Modulation of fibrinolytic response to venous occlusion in humans by a combination of low dose aspirin and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology 12(10):1191-1197.
- Innis SM. 2007. Dietary (n-3) fatty acids and brain development. The Journal of Nutrition 137(4):855-859.
- Institute of Medicine Committee on Nutrient Relationships in Seafood Selection to Balance Benefits and Risks, Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine. 2007. Seafood Choices: Balancing Benefits and Risks. Washington (DC): National Academies Press.
- Iso H, Rexrode KM, Stampfer MJ, Manson JE, Colditz GA, Speizer FE, Hennekens CH. 2001. Intake of fish and omega-3 fatty acids and risk of stroke in women. The Journal of the American Medical Association 285(3):304-312.
- Johansen O, Brekke M, Seljeflot I, Abdelnoor M, Arnesen H. 1999. n-3 fatty acids do not prevent restenosis after coronary angioplasty: results from the CART study. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 33(6):1619-1626.
- Johnson EJ, Chung HY, Caldarella SM, Snodderly DM. 2008. The influence of supplemental lutein and docosahexaenoic acid on serum, lipoproteins, and macular pigmentation. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 87(5):1521-1529.
- Kalmijn S, van Boxten PJ, Ocke M, Verschuren WMM, Kromhout D, Launer LJ. 2004. Dietary intake of fatty acids and fish in relation to cognitive performance at middle age. Neurology 62(2):275-280.
- Kalmijn S, Feskens EJ, Launer LJ, Kromhout D. 1997. Polyunsaturated fatty acids, antioxidants, and cognitive function in very old men. American Journal of Epidemiology 145(1):33-41.
- Kaul U, Sanghvi S, Bahl VK, Dev V, Wasir HS. 1992. Fish oil supplements for prevention of restenosis after coronary angioplasty. International Journal of Cardiology 35(1):87-93.
- Kelley DS, Siegel D, Vemuri M, Mackey BE. 2007. Docosahexaenoic acid supplementation improves fasting and postprandial lipid profiles in hypertriglyceridemic men. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 86(2):324-333.
- Kidd PM. 2007. Omega-3 DHA and EPA for cognition, behavior, and mood: clinical findings and structural-functional synergies with cell membrane phospholipids. Alternative Medical Review 12(3):207-227.
- Kjeldsen-Kragh J, Lund JA, Riise T, Finnanger B, Haaland K, Finstad R, Mikkelsen K, Førre Ø. 1992. Dietary omega-3 fatty acid supplementation and naproxen treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The Journal of Rheumatology 19(10):1531-1536.
- Kotani S, Sakaguchi E, Warashina S, Matsukawa N, Ishikura Y, Kiso Y, Sakakibara M, Yoshimoto T, Guo J, Yamashima T. 2006. Dietary supplementation of arachidonic and docosahexaenoic acids improves cognitive dysfunction. Neuroscience Research 56(2):159-164.
- Kremer JM, Bigauoette J, Michalek AV, Timchalk MA, Lininger L, Rynes RI, Huyck C, Zieminski J, Bartholomew LE. 1985. Effects of manipulation of dietary fatty acids on clinical manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 1(8422):184-187.
- Kremer JM, Lawrence DA, Jubiz W, DiGiacomo R, Rynes R, Bartholomew LE, Sherman M. 1990. Dietary fish oil and olive oil supplementation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and immunologic effects. Arthritis and Rheumatism 33(6):810-819.
- Kremer JM, Lawrence DA, Petrillo GF, Litts LL, Mullaly PM, Rynes RI, Stocker RP, Parhami N, Greenstein NS, Fuchs BR, Mathur A, Robinson DR, Sperling RI, Bigaouette J. 1995. Effects of high-dose fish oil on rheumatoid arthritis after stopping nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Arthritis & Rheumatism 38(8):1107-1114.
- Krokan HE, Bjerve KS, Mork E. 1993. The enteral bioavailability of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid is as good from ethyl esters as from glyceryl esters in spite of lower hydrolytic rates by pancreatic lipase in vitro. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1168(1):59-67.
- Kyrozis A, Psaltopoulou T, Stathopoulos P, Trichopoulos D, Vassilopoulos D, Trichopoulou A. 2009. Dietary lipids and geriatric depression scale score among elders: the EPIC-Greece cohort. Journal of Psychiatric Research 43(8):763-769..
- Lau CS, McLaren M, Belch JJ. 1995. Effects of fish oil on plasma fibrinolysis in patients with mild rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 13(1):87-90.
- Lau CS, Morley KD, Belch JJ. 1993. Effects of fish oil supplementation on non-steroidal antiinflammatory drug requirement in patients with mild rheumatoid arthritis - a double-blind placebo controlled study. British Journal of Rheumatology 32(11):982-989.
- Lauritzen L, Kjaer TM, Fruekilde MB, Michaelsen KF, Frokiaer H. 2005. Fish oil supplementation of lactating mothers affects cytokine production in 2 ½-year-old children. Lipids 40(7):669-676.
- Lawson LD, Hughes BG. 1988. Absorption of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid from fish oil triacylglycerols or fish oil ethyl esters co-ingested with a high-fat meal. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 156(2):960-963.
- Leaf A, Jorgensen MB, Jacobs AK, Cote G, Schoenfeld DA, Scheer J, Weiner BH, Slack JD, Kellett MA, Raizner AE, Weber PC, Mahrer PR, Rossouw JE. 1994. Do fish oils prevent coronary angioplasty? Circulation 90(5):2248-2257.
- Leigh-Firbank EC, Minihane AM, Leake DS, Wright JW, Murphy MC, Griffin BA, Williams CM. 2002. Eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid from fish oils: differential associations with lipid responses. The British Journal of Nutrition 87(5):435-445.
- Lewin GA, Schachter HM, Yuen D, Merchant P, Mamaladze V, Tsertsvadze A, Clifford T, Kourad K, Barnes D, Armour T, Yazdi F, MacNeil J, McGahern C, Senechal H, Fang M, Barrowman N, Sampson M, Morrison A, Elien D, Saint-Martin M, Sambasivan A, Lowcock E, Pan Y, Lemyre B. 2005. Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Child and Maternal Health. Summary, Evidence Report/Technology Assessment No. 118. AHRQ No. 05-E025-2. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
- Linday LA, Dolitsky JN, Shindledecker RD. 2004. Nutritional supplements as adjunctive therapy for children with chronic/recurrent sinusitis: pilot research. International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology 68(6):785-793.
- Llorente AM, Jensen CL, Voigt RG, Fraley JK, Berretta MC, Heird WC. 2003. Effect of maternal docosahexaenoic acid supplementation on postpartum depression and information processing. American Journal Obstetrics and Gynecology 188(5):1348-1353.
- Logan AC. 2004. Review: omega-3 fatty acids and major depression: a primer for the mental health professional. Lipids in Health and Disease 3(25):1-8.
- Lorenz R, Spengler U, Fischer S, Duhm J, Weber PC. 1983. Platelet function, thromboxanes formation and blood pressure control during supplementation of the western diet with cod liver oil. Circulation 67(3):504-511.
- MacLean CH, Issa AM, Newberry SJ, Mojica WA, Morton SC, Garland RH, Hilton LG, Traina SB, Shekelle PG. 2005. Effects of omega-3 fatty acids on cognitive function with aging, dementia, and neurological diseases. Summary, Evidence Report/Technology Assessment No. 114. AHRQ No. 05-E011-2. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
- MacLean CH, Mojica WA, Morton SC, Pencharz J, Hasenfeld Garland R, Tu W, Newberry SJ, Jungvig LK, Grossman J, Khanna P, Rhodes S, Shekelle P. 2004. Effects of omega-3 fatty acids on lipids and glycemic control in type II diabetes and the metabolic syndrome and on inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis, renal disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, and osteoporosis. Summary, Evidence Report/Technology Assessment No. 89. AHRQ No. 04E012-2. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
- MacLean CH, Newberry SJ, Mojica WA, Issa A, Khanna P, Lim YW, Morton SC, Suttorp M, Tu W, Hilton LG, Garland RH, Traina SB, Shekelle PG. 2005. Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Cancer. Summary, Evidence Report/Technology Assessment No. 113. AHRQ No. 05-E010-2. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
- Maes M, Christophe A, Delanghe J, Altamura C, Neels H, Meltzer HY. 1999. Lowered omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in serum phospholipids and cholesterol esters of depressed patients. Psychiatry Research 85(3):275-291.
- Maes M, Mihaylova I, Kubera M, Bosmans E. 2007. Why fish oils may not always be adequate treatments for depression or other inflammatory illnesses: docosahexaenoic acid, an omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid, induces a Th-1-like immune response. Neuroendocrinology Letters 28(6):875-880.
- Maes M, Mihaylova I, Leunis JC. 2005. In chronic fatigue syndrome, the decreased levels of omega-3 poly-unsaturated fatty acids are related to lowered serum zinc and defects in T cell activation. Neuroendocrinology Letters 26(6):745-751.
- Maillard V, Bougnoux P, Ferrari P, Jourdan ML, Pinault M, Lavillonnière M, Body G, Le Floch O, Chajès V. 2002. n-3 and n-6 fatty acids in breast adipose tissue and relative risk of breast cancer in a case-control study in Tours, France. International Journal of Cancer 98(1):78-83.
- Makrides M. 2008. Commentary: outcomes for mothers and their babies: do n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids and seafoods make a difference? Journal of the American Dietetic Association 108(10):1622-1626.
- Marangell LB, Martinez JM, Zboyan HA, Chong H, Puryear LJ. 2004. Omega-3 fatty acids for the prevention of postpartum depression: negative data from a preliminary, open-label pilot study. Depression and Anxiety 19(1):20-23.
- Marangell LB, Martinez JM, Zboyan HA, Kertz B, Kim HF, Puryear LJ. 2003. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid in the treatment of major depression. American Journal Psychiatry 160(5):996-998.
- Maresta A, Balduccelli M, Varani E, Marzilli M, Galli C, Heiman F, Lavezzari M, Stragliotto E, De Caterina R; ESPRIT Investigators. 2002. Prevention of postcoronary angioplasty restenosis by omega-3 fatty acids: main results of the Esapent for Prevention of Restenosis ITalian study (ESPRIT). American Heart Journal 143(6):E5.
- Martin RE, Carter EP, Flick GJ, Davis LM, editors. 2000. Marine & Freshwater Products Handbook. Lancaster (PA): Technomic Publishing Company, Inc.
- McCann JC, Ames BN. 2005. Is docosahexaenoic acid, an n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid, required for development of normal brain function? An overview of evidence from cognitive and behavioral tests in humans and animals. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 82(2):281-295.
- Meydani M, Natiello F, Goldin B, Free N, Woods M, Schaefer E, Blumberg JB, Gorbach SL. 1991. Effect of long-term fish oil supplementation on vitamin E status and lipid peroxidation in women. Journal of Nutrition 121(4):484-491.
- Mickleborough TD, Ionescu AA, Rundell KW. 2004. Omega-3 fatty acids and airway hyperresponsiveness in asthma. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine 10(6):1067-1075.
- Mickleborough TD, Lindley MR, Ionescu AA, Fly AD. 2006. Protective effect of fish oil supplementation on exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in asthma. Chest 129(1):39-49.
- Mihrshahi S, Peat JK, Webb K, Oddy W, Marks GB, Mellis CM. 2004. Effect of omega-3 fatty acid concentrations in plasma on symptoms of asthma at 18 months of age. Pediatric Allergy and Immunology 15(6):517-522.
- Montgomery C, Speake BK, Cameron A, Sattar N, Weaver LT. 2003. Maternal docosahexaenoic acid supplementation and fetal accretion. The British Journal of Nutrition 90(1):135-140.
- Moore CS, Bryant SP, Mishra GD, Krebs JD, Browning LM, Miller GJ, Jebb SA. 2006. Oily fish reduces plasma triacylglycerols: a primary prevention study in overweight men and women. Nutrition 22(10):1012-1024.
- Mori TA, Bao DQ, Burke V, Puddey IB, Beilin LJ. 1999. Docosahexaenoic acid but not eicosapentaenoic acid lowers ambulatory blood pressure and heart rate in humans. Hypertension 34(2):253-260.
- Mori TA, Burke V, Puddey IB, Watts GF, O'Neal DN, Best JD, Beilin LJ. 2000. Purified eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids have differential effects on serum lipids and lipoproteins, LDL particle size, glucose, and insulin in mildly hyperlipidemic men. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 71(5):1085-1094.
- Morris MC, Sacks F, Rosner B. 1993. Regulation of blood pressure: does fish oil lower blood pressure? A meta-analysis of controlled trials. Circulation 8(2):523-533.
- Mueller BA, Talbert RL, Tegeler CH, Prihoda TJ. 1991. The bleeding time effects of a single dose of aspirin in subjects receiving omega-3 fatty acid dietary supplementation. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 31(2):185-190.
- Nagakura T, Matsuda S, Shichijyo K, Sugimoto H, Hata K. 2000. Dietary supplementation with fish oil rich in ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in children with bronchial asthma. European Respiratory Journal 16(5):861-865.
- Nakamura K, Kariyazono H, Komokata T, Hamada N, Sakata R, Yamada K. 2005. Influence of preoperative administration of ω-3 fatty acid-enriched supplement on inflammatory and immune responses in patients undergoing major surgery for cancer. Nutrition 21(6):639-645.
- Nelson GJ, Schmidt PS, Bartolini GL, Kelley DS, Kyle D. 1997. The effect of dietary docosahexaenoic acid on platelet function, platelet fatty acid composition, and blood coagulation in humans. Lipids 32(11):1129-1136.
- Nemets B, Osher Y, Belmaker RH. 2004. Omega-3 fatty acids and augmentation strategies in treating resistant depression. Essential Psychopharmacology 6(1):59-64.
- Nemets H, Nemets B, Apter A, Bracha Z, Belmaker RH. 2006. Omega-3 treatment of childhood depression: a controlled, double-blind pilot study. American Journal of Psychiatry 163(6):1098-1100.
- Nemets B, Stahl Z, Belmaker RH. 2002. Addition of omega-3 fatty acid to maintenance medication treatment for recurrent unipolar depressive disorder. American Journal of Psychiatry 159(3):477-479.
- Nettleton JA, Katz R. 2005. n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in type 2 diabetes: a review. Journal of the American Dietetic Association 105(3):428-440.
- Nielsen GL, Faarvang KL, Thomsen BS, Teglbjærg KL, Jensen LT, Hansen TM, Lervang HH, Schmidt EB, Dyerberg J, Ernst E. 1992. The effects of dietary supplementation with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, double blind trial. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 22(10):687-691.
- Noaghiul S, Hibbeln JR. 2003. Review: Cross-national comparisons of seafood consumption and rates of bipolar disorders. The American Journal of Psychiatry 160(12):2222-2227.
- Nordoy A, Barstad L, Connor WE, Hatcher L. 1991. Absorption of the n-3 eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids as ethyl esters and triglycerides by humans. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 53(5):1185-1190.
- Nordström DC, Honkanen VE, Nasu Y, Antila E, Friman C, Konttinen YT. 1995. Alphalinolenic acid in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. A double-blind, placebo-controlled and randomized study: flaxseed vs. safflower seed. Rheumatology International 14(6):231-234.
- O'Connor GT, Malenka DJ, Olmstead EM. 1992. A meta-analysis of randomized trials of fish oil in prevention of restenosis following coronary angioplasty. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 8(3):186-192.
- Olafsdottir AS, Magnusardottir AR, Thorgeirsdottir H, Hauksson A, Skuladottir GV, Steingrimsdottir L. 2005. Relationship between dietary intake of cod liver oil in early pregnancy and birthweight. BJOG: an International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 112(4):424-429.
- Olsen SF, Secher NJ. 2002. Low consumption of seafood in early pregnancy as a risk factor for preterm delivery: prospective cohort study. British Medical Journal 324(7335):447-450.
- Onwude JL, Lilford RJ, Hjartardottir H, Staines A, Tuffnell D. 1995. A randomised double blind placebo controlled trial of fish oil in high risk pregnancy. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 102(2):95-100.
- Osher Y, Bersudsky U, Belmaker, RH. 2005. Omega-3 eicosapentaenoic acid in bipolar depression: report of a small open-label study. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 66(6):726-729.
- Parker G G, Gibson NA, Brotchie H, Heruc G, Rees AM, Hadzi-Pavlovic D. 2006. Review: omega-3 fatty acids and mood disorders. American Journal of Psychiatry 163(6):969-978.
- Paus T, Zijdenbos A, Worsley K, Collins DL, Blumenthal J, Giedd JN, Rapoport JL, Evans AC. 1999. Structural maturation of neural pathways in children and adolescents: in vivo study. Science 283(5409):1908-1911.
- Pawlosky RJ, Bacher J, Salem N. 2001. Ethanol consumption alters electroretinograms and depletes neural tissues of docosahexaenoic acid in rhesus monkeys: nutritional consequences of a low n-3 fatty acid diet. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 25(12):1758-1765.
- Peat JK, Mihrshahi S, Kemp AS, Marks GB, Tovey ER, Webb K, Mellis CM, Leeder SR. 2004. Three-year outcomes of dietary fatty acid modification and house dust mite reduction in the Childhood Asthma Prevention Study. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 114(4):807-813.
- Pedersen HS, Mulvad G, Seidelin KN, Malcom GT, Boudreau DA. 1999. N-3 fatty acids as a risk factor for haemorrhagic stroke. Lancet 353(9155):812-813.
- Peet M. 2003. Eicosapentaenoic acid in the treatment of schizophrenia and depression: rationale and preliminary double-blind clinical trial results. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes, and Essential Fatty Acids 69(6):477-485.
- Picado C, Castillo JA, Schinca N, Pujades M, Ordinas A, Coronas A, Agusti-Vidal A. 1988. Effects of a fish oil enriched diet on aspirin intolerant asthmatic patients: a pilot study. Thorax 43(2):93-97.
- Radack K, Deck C, Huster G. 1990. The comparative effects of n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids on plasma fibrinogen levels: a controlled clinical trial in hypertriglyceridemic subjects. Journal of the American College of Nutrition 9(4):352-357.
- Raitt MH, Connor WE, Morris C, Kron J, Halperin B, Chugh SS, McClelland J, Cook J, MacMurdy K, Swenson R, Connor SL, Gerhard G, Kraemer DF, Oseran D, Marchant C, Calhoun D, Shnider R, McAnulty J. 2005. Fish oil supplementation and risk of ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation in patients with implantable defibrillators: a randomized controlled trial. The Journal of the American Medical Association 293(23):2884-2891.
- Reddy BS. 2004. Omega-3 fatty acids in colorectal cancer prevention. International Journal of Cancer 112(1):1-7.
- Reis GJ, Silverman DI, Boucher TM, Sipperly ME, Horowitz GL, Sacks FM, Pasternak RC. 1990. Effects of two types of fish oil supplements on serum lipids and plasma phospholipids fatty acids in coronary artery disease. The American Journal of Cardiology 15(66):1171-1175.
- Richardson AJ. 2004. Clinical trials of fatty acid treatment in ADHD, dyslexia, dyspraxia and the autistic spectrum. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes, and Essential Fatty Acids 70(4):383-390.
- Richardson AJ, Montgomery P. 2005. The Oxford-Durham study: a randomized, controlled trial of dietary supplementation with fatty acids in children with developmental coordination disorder. Pediatrics 115(5):1360-1366.
- Richardson AJ, Puri BK. 2002. A randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the effects of supplementation with highly unsaturated fatty acids on ADHD-related symptoms in children with specific learning difficulties. Progress in Neuropsychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry 26(2):233-239.
- Richardson AJ, Puri BK. 2000. The potential role of fatty acids in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes, and Essential Fatty Acids 63(1-2):79-87.
- Rose DP, Connolly JM. 1999. Omega-3 fatty acids as cancer chemopreventive agents. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 83(3):217-244.
- Ryan AS, Nelson EB. 2008. Assessing the effect of docosahexaenoic acid on cognitive functions in healthy preschool children: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Clinical Pediatrics 47(4):355-362.
- Sagduyu K, Docucu ME, Eddy BA, Craigen G, Baldassano CF, Y1ldlz A. 2005. Omega-3 fatty acids decreased irritability of patients with bipolar disorder in an add-on, open label study. Nutrition Journal 4:6.
- Sagredos AN. 1991. [Fatty Acid Composition of Fish Oil Capsules]. Fett Wissenschaft Technologie 93(5):184-191 [article in German].
- Samieri C, Feart C, Letenneur L, Dartigues JF, Peres K, Auriacombe S, Peuchant E, Delcourt C, Barberger-Gateau P. 2008. Low plasma eicosapentaenoic acid and depressive symptomatology are independent predictors of dementia risk. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 88(3):714-721.
- Sanders TA, Hinds A. 1992. The influence of a fish oil high in docosahexaenoic acid on plasma lipoprotein and vitamin E concentrations and haemostatic function in healthy male volunteers. The British Journal of Nutrition 68(1):163-173.
- Saynor R, Gillott T. 1992. Changes in blood lipids and fibrinogen with a note on safety in a long term study on the effects of n-3 fatty acids in subjects receiving fish oil supplements and followed for seven years. Lipids 27(7):533-538.
- Schachter HM, Kourad K, Merali Z, Lumb A, Tran K, Miguelez M, Lewin G, Sampson M, Barrowmann N, Senechal H, McGahern C, Zhang L, Morrison A, Shlik J, Pan Y, Lowcock EC, Gaboury I, Bradejn J, Duffy A. 2005. Effects of omega-3 fatty acids on mental health. Summary, Evidence Report/Technology Assessment No. 116. AHRQ No. 05-E022-2. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
- Schmidt EB, Lervang HH, Varming K, Madsen P, Dyerberg J. 1992. Long-term supplementation with n-3 fatty acids, I: effect on blood lipids, haemostasis and blood pressure. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation 52(3):221-228.
- Schwellenbach LJ, Olson KL, McConnell KJ, Stolcpart RS, Nash JD, Merenich JA. 2006. The triglyceride-lowering effects of a modest dose of docosahexaenoic acid alone versus in combination with low dose eicosapentaenoic acid in patients with coronary artery disease and elevated triglycerides. Journal of the American College of Nutrition 25(6):480-485.
- Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition, Foods Standard Agency, Department of Health. Advice on Fish Consumption: Benefits and Risks 2004. London (GB): TSO (The Stationery Office). [Accessed 2023 March 07]. Available from: https://cot.food.gov.uk/sites/default/files/cot/fishreport200401.pdf
- Silverman DI, Ware JA, Sacks FM, Pasternak RC. 1991. Comparison of the absorption and effect of on platelet function of a single dose of n-3 fatty acids given as fish or fish oil. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 53(5):1165-1170.
- Silvers KM, Woolley CC, Hamilton FC, Watts PM, Watson RA. 1999. Randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial of fish oil in the treatment of depression. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes, and Essential Fatty Acids 72(3):211-218.
- Simons LA, Parfitt A, Simons J, Balasubramaniam S. 1990. Effects of an ethyl ester preparation of fish oils (Himega) on lipids and lipoproteins in hyperlipidaemia. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Medicine 20(5):689-694.
- Simopoulos AP, Leaf A, Salem N. 1999. Workshop on the essentiality of and recommended dietary intakes for omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids. Journal of the American College of Nutrition 18(5):487-489.
- Singh M. 2005. Essential fatty acids, DHA and human brain. Indian Journal of Pediatrics 72(3):239-242.
- Sinn N, Bryan J. 2007. Effect of supplementation with polyunsaturated fatty acids and micronutrients on learning and behavior problems associated with child ADHD. Journal of Development and Behavioural Pediatrics 28(2):82-91.
- Solfrizzi V, Colacicco AM, D'Introno A, Capurso C, Del Parigi A, Capurso SA, Argentieri G, Capurso A, Panza F. 2006. Dietary fatty acids intakes and rate of mild cognitive impairment. The Italian Longitudinal Study on Aging. Experimental Gerontology 41(6):619-627.
- Stehr SN, Heller AR. 2006. Omega-3 fatty acid effects on biochemical indices following cancer surgery. Clinica Chimica Acta 373(1-2):1-8.
- Stevens LJ, Zentall SS, Abate ML, Kuczek T, Burgess JR. 1996. Omega-3 fatty acids in boys with behavior, learning and health problems. Physiology and Behavior 59(4-5):915-920.
- Stevens LJ, Zentall SS, Deck JL, Abate ML, Watkins BA, Lipp SR, Burgess JR. 1995. Essential fatty acid metabolism in boys with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 62(4):761-768.
- Stevens L, Zhang W, Peck L, Kuczek T, Grevstad N, Mahon A, Zentall SS, Arnold LE, Burgess JR. 2003. EFA supplementation in children with inattention, hyperactivity, and other disruptive behaviors. Lipids 38(10):1007-1021.
- Stoll AL, Severus WE, Freeman MP, Rueter S, Zboyan HA, Diamond E, Cress KK, Marangell LB. 1999. Omega 3 fatty acids in bipolar disorder: a preliminary double blind, placebo-controlled trial. Archives of General Psychiatry 56(5):407-412.
- Studer M, Briel M, Leimenstoll B, Glass TR, Bucher HC. 2005. Effect of different antilipidemic agents and diets on mortality: a systematic review. Archives of Internal Medicine 165(7):725-730.
- Su K, Huang S, Chiu C, Shen WW. 2003. Omega-3 fatty acids in major depressive disorder. A preliminary double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. European Neuropsychopharmacology 13(4):267-271.
- Sundrarjun T, Komindr S, Archararit N, Dahlan W, Puchaiwatananon O, Angthararak S, Udomsuppayakul U, Chuncharunee S. 2004. Effects of n-3 fatty acids on serum interleukin-6, tumour necrosis factor-α, and soluble tumour necrosis factor receptor p55 in active rheumatoid arthritis. The Journal of International Medical Research 32(5):443-454.
- Svensson M, Schmidt EB, Jørgensen KA, Christensen JH. 2006. N-3 fatty acids as secondary prevention against cardiovascular events in patients who undergo chronic hemodialysis: a randomized, placebo-controlled intervention trial. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1(4):780-786.
- Szajewska H, Horvath A, Koletzko B. 2006. Effect of n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation of women with low-risk pregnancies on pregnancy outcomes and growth measures at birth: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 83(6):1337-1344.
- Takemura Y, Sakurai Y, Honjo S, Tokimatsu A, Gibo M, Hara T, Kusakari A, Kugai N. 2002. The relationship between fish intake and the prevalence of asthma: the Tokorozawa Childhood Asthma and Pollinosis Study. Preventive Medicine 34(2):221-225.
- Takezaki T, Inoue M, Kataoka H, Ikeda S, Yoshida M, Ohashi Y, Tajima K, Tominaga S. 2003. Diet and lung cancer risk from a 14-year population-based prospective study in Japan: with special reference to fish consumption. Nutrition and Cancer 45(2):160-167.
- Takwale A, Tan E, Agarwal S, Barclay G, Ahmed I, Hotchkiss K, Thompson JR, Chapman T, Berth-Jones J. 2003. Efficacy and tolerability of borage oil in adults and children with atopic eczema: randomised, double blind, placebo controlled, parallel group trial. British Medical Journal 327(7428):1385.
- Tanskanen A, Hibbeln JR, Tuomilehto J, Uutela A, Haukkala A, Viinamaki H, Lehtonen J, Vartiainen E. 2001. Fish consumption and depressive symptoms in the general population in Finland. Psychiatric Services 52(4):529-531
- Terry PD, Terry JB, Rohan TE. 2004. Long-chain (n-3) fatty acid intake and risks of cancers of the breast and the prostate: recent epidemiological studies, biological mechanisms, and directions for future research. Journal of Nutrition 134(Suppl 12):3412S-3420S.
- Theobald HE, Goodall AH, Sattar N, Talbot DC, Chowienczyk PJ, Sanders TA. 2007. Low-dose docosahexaenoic acid lowers diastolic blood pressure in middle-aged men and women. Journal of Nutrition 137(4):973-978.
- Theodoratou E, McNeill G, Cetnarskyj R, Farrington SM, Tenesa A, Barnetson R, Porteous M, Dunlop M, Campbell H. 2007. Dietary fatty acids and colorectal cancer: a case-control study. American Journal of Epidemiology 166(2):181-195.
- Thies F, Nebe-von-Caron G, Powell JR, Yaqoob P, Newsholme EA, Calder PC. 2001. Dietary supplementation with eicosapentaenoic acid, but not with other long-chain n-3 or n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids, decreases natural killer cell activity in healthy subjects aged >55 y. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 73(3):539-548.
- Tsekos E, Reuter C, Stehle P, Boeden G. 2004. Perioperative administration of parenteral fish oil supplements in a routine clinical setting improves patient outcome after major abdominal surgery. Clinical Nutrition 23(3):325-330.
- Tulleken JE, Limburg PC, Muskiet FA, van Rijswijk MH. 1990. Vitamin E status during dietary fish oil supplementation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 33(9):1416-1419.
- Tulleken JE, Limburg PC, van Rijswijk MH. 1988. Fish oil and plasma fibrinogen. British Medical Journal 297(6648):615-616.
- Uauy R, Hoffman DR, Mena P, Llanos A, Birch EE. 2003. Term infant studies of DHA and ARA supplementation on neurodevelopment: results of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Pediatrics 143(Suppl 4):S17-S25
- Vaisman N, Kaysar N, Zaruk-Adasha Y, Pelled D, Brichon G, Zwingelstein G, Bodennec J. 2008. Correlation between changes in blood fatty acid composition and visual sustained attention performance in children with inattention: effect of dietary n-3 fatty acids containing phospholipids. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 87(5):1170-1180.
- Valagussa F, Franzosi MG, Geraci E, Mininni N, Nicolosi GL, Santini M, Tavazzi L, Vecchio C. 1999. Dietary supplementation with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and vitamin E after myocardial infarction: results of the GISSI-Prevenzione trial. Lancet 354(9177):447-455.
- Valk EE, Hornstra G. 2000. Relationship between vitamin E requirement and polyunsaturated fatty acid intake in man: a review. International Journal for Vitamin and Nutrition Research 70(2):31-42.
- Van den Berg M, Birnbaum LS, Denison M, De Vito M, Farland W, Feeley M, Fiedler H, Hakansson H, Hanberg A, Haws L, Rose M, Safe S, Schrenk D, Tohyama C, Tritscher A, Tuomisto, M. Tysklind J, Walker N, Peterson RE. REVIEW The 2005 World Health Organization reevaluation of human and mammalian toxic equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. Toxicological Sciences 2006;93(2):223-241.
- van de Rest O, Geleijnse JM, Kok FJ, van Staveren WA, Hoefnagels WH, Beekman ATF, de Groot LCPGM. 2008. Effect of fish-oil supplementation on mental well-being in older subjects: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 88(3):706-713.
- Van der Tempel H, Tulleken JE, Limburg PC, Muskiet FA, van Rijswijk MH. 1990. Effects of fish oil supplementation in rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 49(2):76-80.
- van Gelder BM, Tijhuis M, Kalmijn S, Kromhout D. 2007. Fish consumption, n-3 fatty acids, and subsequent 5-y cognitive decline in elderly men: the Zutphen Elderly Study. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 85(4):1142-1147.
- van Gool CJ, Thijs C, Henquet CJ, van Houwelingen AC, Dagnelie PC, Schrander J, Menheere PP, van den Brandt PA. 2003. Gamma-linolenic acid supplementation for prophylaxis of atopic dermatitis-a randomized controlled trial in infants at high familial risk. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 77(4):943-951.
- Velho S, Marques-Vidal P, Baptista F, Camilo ME. 2008. Dietary intake adequacy and cognitive function in free-living active elderly: a cross-sectional and short-term prospective study. Clinical Nutrition 27(1):77-86.
- Velzing-Aarts FV, van der Klis FR, van der Dijs FP, van Beusekom CM, Landman H, Capello JJ, Muskiet FA. 2001. Effect of three low-dose fish oil supplements, administered during pregnancy, on neonatal long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid status at birth. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes, and Essential Fatty Acids 65(1):51-57.
- Vidgren HM, Ågren JJ, Schwab U, Rissanen T, Hänninen O, Uusitupa MI. 1997. Incorporation of n-3 fatty acids into plasma lipid fractions, and erythrocyte membranes and platelets during dietary supplementation with fish, fish oil, and docosahexaenoic acid-rich oil among healthy young men. Lipids 32(7):697-705.
- Visioli F, Risé P, Barassi MC, Marangoni F, Galli C. 2003. Dietary intake of fish vs. formulations leads to higher plasma concentrations of n-3 fatty acids. Lipids 38(4):415-418.
- Vlaandingerbroek H, Hornstra G, Koning TJ, Smeitink JAM, Bakker HD, Klerk HBC, RubioGozalbo ME. 2006. Essential polyunsaturated fatty acids in plasma and erythrocytes of children with inborn errors of amino acid metabolism. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism 88(2):159-165.
- Voigt RG, Llorente AM, Jensen CL, Fraley JK, Berretta MC, Heird WC. 2001. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of docosahexaenoic acid supplementation in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. The Journal of Pediatrics 139(2):189-196.
- Von Schacky C, Fischer S, Weber PC. 1985. Long-term effects of dietary marine ω-3 fatty acids upon plasma and cellular lipids, platelet function, and eicosanoid formation in humans. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 76(4):1626-1631.
- Von Schacky C, Weber PC. 1985. Metabolism and effects on platelet function of the purified eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids in humans. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 76(6):2446-2450.
- Walker T, Singh PK, Wyatt KM, O'Brien PM. 1999. The effect of prostanoid precursors and inhibitors on platelet angiotensin II binding. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 19(1):56-58.
- Wang W, Shinto L, Connor WE, Quinn JF. 2008. Nutritional biomarkers in Alzheimer's disease: the association between carotenoids, n-3 fatty acids, and dementia severity. Journal of Alzheimers Disease 13(1):31-38.
- Westenhoefer J, Bellisle F, Blundell JE, de Vries J, Edwards D, Kallus W, Milon H, Pannemans D, Tuijtelaars S, Tuorila H. 2004. PASSCLAIM - mental state and performance. European Journal of Nutrition 43(Suppl 2):ll/85-ll/117.
- Whalley LJ, Fox HC, Wahle KW, Starr JM, Deary IJ. 2004. Cognitive aging, childhood intelligence, and the use of food supplements: possible involvement of n-3 fatty acids. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 80(6):1650-1657.
- Whelton SP, He J, Whelton PK, Muntner P. 2004. Meta-analysis of observational studies of fish intake and coronary heart disease. The American Journal of Cardiology 93(9):1119-1123.
- Wohl DA, Tien HC, Busby M, Cunningham C, Macintosh B, Napravnik S, Danan E, Donovan K, Hossenipour M, Simpson RJ Jr. 2005. Randomized study of the safety and efficacy of fish oil (omega-3 fatty acid) supplementation with dietary and exercise counselling for the treatment of antiretroviral therapy-associated hypertriglyceridemia. Clinical Infectious Diseases 41(10):1498-1504.
- Wong KW. 2005. Clinical efficacy of n-3 fatty acid supplementation in patients with asthma. Journal of the American Dietetic Association 105(1):98-105.
- Woodman RJ, Mori TA, Burke V, Puddey IB, Barden A, Watts GF, Beilin LJ. 2003. Effects of purified eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid on platelet, fibrinolytic and vascular function in hypertensive type 2 diabetic patients. Atherosclerosis 166(1):85-93.
- Woodman RJ, Mori TA, Burke V, Puddey IB, Watts GF, Beilin LJ. 2002. Effects of purified eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids on glycemic control, blood pressure, and serum lipids in type 2 diabetic patients with treated hypertension. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 76(5):1007-1015.
- Yehuda S, Rabinovich S, Mostofsky DI.1998. Modulation of learning and neuronal membrane composition in the rat by essential fatty acid preparation: time-course analysis. Neurochemical Research 23(5):627-634.
- Yzebe D, Lievre M. 2004. Fish oils in the care of coronary heart disease patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Fundamental & Clinical Pharmacology 18(5):581-592.